Pain in the abdominal muscles
Abdominal muscle pain, Abdominal muscle tear
Abdominal pain can have many causes. In this article we will focus primarily on the pain from the abdominal muscles.
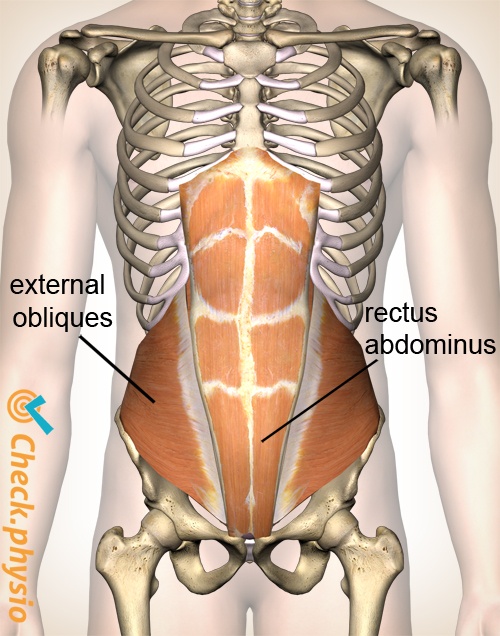
The abdominal wall is formed by the skin, muscles, fascia, fatty tissue and the peritoneum that lines the front and sides of the abdomen. Any of these structures can be affected when we discuss abdominal pain. The organs located in the abdomen can also be a possible source of abdominal pain.
Description of the condition
Pain that becomes worse when the abdominal muscles are tensed usually indicates a problem with the abdominal wall. Sometimes a portion of the peritoneum (membrane which lines the abdominal cavity) will protrude through a weak spot or opening in the abdominal wall. This is called an abdominal hernia. Damage to the nerves in the abdomen can also cause abdominal pain. In athletes, the pain is often caused by the muscles.
The muscle pain is often caused by the rectus abdominis muscles (abdominals or abs) that allow the trunk to bend. They are located in the area around the navel. If the oblique abdominal muscles are damaged, the pain is located more to the side of the abdomen. The oblique abdominal muscles assist in the twisting movements of the upper body.
Cause and origin
Spraining, tearing or overloading of the abdominal muscles can have various causes. Often the muscle pain will occur after exercising the abdominal muscles, for example after performing sit-ups. Sudden twisting movements of the body can also cause prolonged abdominal pain. When somebody slips and loses balance, the abdominal muscles contract as a reflex action. Excessive forces can cause damage to the muscle.
Signs & symptoms
- Pain when contracting the abdominal muscles.
- Pain when lifting outstretched legs whilst lying on the back.
- Lifting the head and shoulders whilst lying on the back is painful.
- Laughing and coughing can make the pain worse.
Generally, there is no nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, fever, altered bowel movements or pain depending on what is eaten. If any of the above symptoms do occur, this pain could originate in the abdominal cavity instead of the abdominal wall. There may be a problem with the intestines or other internal organs.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Muscle pain after strength training for the abdominal muscles usually disappears within a few days. If the pain persists, or if there is any doubt about the cause of the symptoms, then it is wise to consult a doctor or physiotherapist.
Exercises
You can check your symptoms using the online physiotherapy check or make an appointment with a physiotherapy practice in your area.
References
Brukner, P. & Khan, K. (2016). Clinical sports medicine (Nederlandse bewerking). 4th edition. Michel van Troost. PreVision, Eindhoven.
Suleiman, S. & Johnston, D.E. (2001). The abdominal wall: An overlooked source of pain. Am Fam Physician. 64(3):431-8.



